Accommodating Unleaded Brass
By recognizing and accommodating for unleaded brasses' lack of lead, and the different thermal conductivity, differences in chip forming, and the need to up-tool for heavier feeds rather than higher speeds, your shop can also be successful at making parts from these newer, more challenging grades.
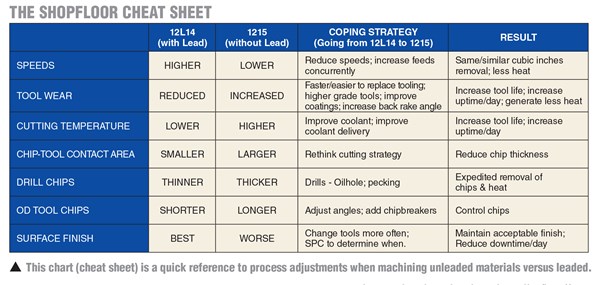
Unleaded brasses are not necessarily harder to run than leaded brass. They are just different. By recognizing and accommodating for their lack of lead, and the different thermal conductivity, differences in chip forming, and the need to up-tool for heavier feeds rather than higher speeds, your shop can also be successful at making parts from these newer, more challenging grades.
It is widely acknowledged that lead promotes machinability. To get the maximum production from automatic machines, additions of lead have been commonly used in metals, particularly steels and brasses. In brass, dispersed in the grain boundaries, lead acts as an internal lubricant: It reduces friction, and thus heat. By reducing the heat, lead allows the metals to which it has been added to be machined at much higher speeds than the comparable non-leaded grades. These higher speeds (rpm or surface feet per minute) result in shorter cycle times to produce each part. Short cycle times mean less expensive parts.
Leaded brass offered these historical advantages:
- Excellent surface finish
- Forgiving of machine mis-adjustments
- No thermal issues
- Fast cycle times
- No chip control issues
When machining non-leaded materials, we have to somehow maintain surface finish, get to commercially feasible cycle times, and deal with less than ideal chip characteristics.
What are some strategies for machining the new unleaded brasses?
Increase the feed. Since we lost the lead and the ability to run at higher speeds, increasing the feed can help us get to equivalent cubic inches of removal rates.
Improve the machine rigidity. Heavier feeds mean that your machine needs to be adjusted and solid. It also means more horsepower required— again mandating a rock-solid setup.
Improve the tool. 4 percent lead is very forgiving of tool quality; the new nonleaded grades are the opposite—they present a number of challenges to your tools. Improved materials, geometry and coatings are key to machining unleaded brasses with minimum issues. Also, they will require fewer replacements, helping to get more net production at the end of the shift.
Improve the chip management. Some unleaded grades replace the lead with zinc, resulting in a grade with a type III chip—stringy and bird’s-nest prone. With these grades, pay special attention to drills selected, and try inserts with chip control features to help you manage that chip.
Deal with the increased heat. The lead helped to reduce friction and heat in the leaded grades. With the lead removed, you will have increased heat generated. Carbide is more forgiving of heat, as are tool coatings. Talk to your supplier of metalworking fluids. Chances are, they will have a fluid that will help manage those extra BTUs and maintain your tools’ edges.
Change your ideas about machining brass. Unleaded brass machines more like steel than brass as long as you think of it like leaded brass, you will fight it. Instead, think of it as just a yellow version of 1215 steel or stainless and your expectations will be much closer to reality.
Unleaded brasses are not necessarily harder to run than leaded brass. They are just different. By recognizing and accommodating for their lack of lead and the resultant different thermal conductivity, differences in chip forming, and the need to up the tool for heavier feeds rather than higher speeds, your shop can also be successful at making parts from these newer, more challenging grades.
The market for our precision machined parts continues to be evolve. Evolve your thinking and processing to adjust to the realities of unleaded materials to remain a viable and preferred supplier.
For more details on grades and recommendations, read Adjusting to Unleaded.
Originally posted on PMPAspeakingofprecision.com blog.
Read Next
A Tooling Workshop Worth a Visit
Marubeni Citizen-Cincom’s tooling and accessory workshop offers a chance to learn more about ancillary devices that can boost machining efficiency and capability.
Read More5 Aspects of PMTS I Appreciate
The three-day edition of the 2025 Precision Machining Technology Show kicks off at the start of April. I’ll be there, and here are some reasons why.
Read MoreDo You Have Single Points of Failure?
Plans need to be in place before a catastrophic event occurs.
Read More







.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)










