Cryogenic Treatment and Cutting Tool Life
All users can say is it works. Why it works is less clear, but this overview paints a better picture.
Successful applications of cryogenic treatment of metals go back decades. Numerous articles have been published touting tool life improvements of 5 times or more compared with untreated cutters.
However, widespread acceptance of this process has been relatively slow in part because deep freezing tools for longer life seems unbelievable, and there is a perceived lack of scientific data to conclusively document what’s actually happening. However, there are theories that explain what happens in ferrous materials and carbide when cryogenically treated, but they fall down when trying to explain why the process works for nonferrous materials.
This article concentrates on cutting tools for metalworking, not golf balls, nylon stockings, plastics and other materials that use cryogenics to enhance their performance characteristics.
Giving it the Treatment
The cryogenic treatment process is relatively simple albeit time consuming. A typical treatment cycle takes around 48 hours to complete. However, time is the key to a proper cryogenic treatment.
Each step is timed usually based on the weight of the parts being treated. The cool-down phase, going from ambient to minus 300-310°F (the temperature of liquid nitrogen) usually runs in a 4- to 6-hour range (1 to 2 degrees per minute). This is followed by a “soak” lasting around 24 hours. Once the parts have soaked, warm up to room temperature is another 4 to 6 hours. Most cryogenic chambers are equipped with a small heater that raises the temperature to almost 300°F for the final couple of hours to ensure there are no “cold” spots in the material and to provide tempering.
Because nitrogen in its gaseous form is used as the cooling agent, parts and tools to be cooled remain dry. During the cool-down phase any oxygen in the chamber is purged by the nitrogen, so no rust can form. Only arrangement of the parts is needed, no fixtures or racks are required.
The flow rate for the nitrogen and the various timed steps are controlled by a computer and use data collected from experience. Once the time temperature information is programmed, the process is automatic. The cryogenic unit looks not unlike a chest freezer or refrigerator.
The tools or other parts come out of the cryogenic unit with no discernible changes in color or cosmetic appearance. No dimensional changes will appear either, with the exception of items that were improperly heat treated prior to the cryogenic treatment, leaving internal stress that may be released during cooling.
According to Bill Groschen, president of Diversified Cryogenics, “This lack of cosmetic change can be a detriment. For many of my customers, the fact that there is no physical change makes some of them doubt the efficacy of the process. However, those doubts disappear when they see the increase in tool life from cryogenic treatment.”
More Than Just a Leap of Faith
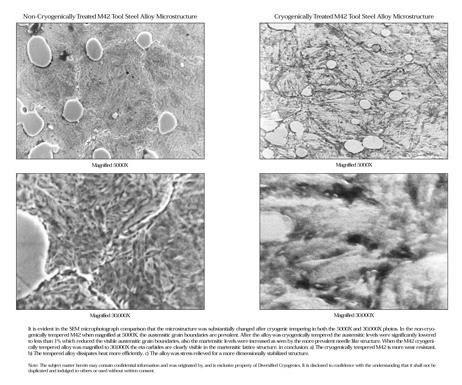
Alloy tool steels such as those used to make end mills, twist drills, reamers and other cutting tools have been the subject of most of the research of the cryogenic treatment effect. The research has demonstrated that using deep cryogenic treatment results typically in a two- to five-fold improvement over the normal life of these tools.
The theory that accounts for these results in cutting tools is widely accepted, mostly because it is based on the known principles of metallurgy. Those principles involve the well-known heat and quench cycle employed for centuries to control the performance characteristics of ferrous materials. Cryogenics simply takes the quench to new lows—minus 300°F.
According to cryogenic treatment research done by Dr. Randall Barron from Louisiana State University, there are two primary mechanisms at work in the cryogenic treatment process. First, he writes, “Super cold treatment seems to convert retained austenite structures in the metal into martensite, which is very hard and brittle. However, the martensite is tempered to provide better toughness properties as the metal returns to room temperature.
“The martensite structure resists plastic deformation much better than an austenite structure because the small atoms in the martensite lattice “lock together” the iron atoms more effectively than in the more open-centered cubic austenite lattice. The slow warming to room temperature from the cryogenic temperatures of minus 320°F tempers the martensite so that it is better able to resist impact than untempered martensite.
Second, Dr. Barron writes, “The cryogenic treatment of high alloy steels, such as tool steels, results in the formation of very small carbide particles dispersed within the martensite structure between the larger carbide particles present in the steel.
“The way these smaller particles act to strengthen the steel is analogous to concrete made from large aggregate versus concrete made from very small aggregate (course sand). The smaller aggregate makes a much stronger concrete mix than one using the larger rocks. The small, hard carbide particles within the martensite matrix help support the matrix and resist penetration by foreign particles in abrasive wear.”
Carbide inserts and form tools also show an increase in wear resistance from cryogenic treatment. Here, the belief is that the carbide inserts shrink slightly during the cool-down phase of the treatment, creating some plastic flow within the micro-voids in between the carbide and the binder. When the carbide returns to ambient temperature, it leaves compressive stresses on the surface of the voids. These compressive stresses, in turn, tend to counteract localized weakening caused by the voids, thereby resulting in an overall improvement in wear resistance.
Make it Part of the Process
Taking advantage of cryogenics can result in significant cost savings from increased tool life. Once a cutter is treated, it is treated for life. In addition to longer time in the cut, these tools wear less, so resharpening requires less material to be removed, so more regrinds can be done. For lights-out operation or lightly tended machining, longer, predictable tool life can make the transition to unmanned operation less stressful.
However, to take full advantage of cryogenic treatment, a shop must include it in the planning process. It’s really no different than sending parts out for plating or coating. The turn around time must be calculated into the delivery schedule.
Likewise, the cryogenic treatment process itself takes 2 days, so the time needed to send cutters to be treated needs to be calculated into the production schedule. Of course, like many machine shops, Diversified Cryogenics included, one can bring the process in-house.
Related Content
Replaceable-Insert Spade Drill Basics, Advantages
Although solid carbide and indexable-insert drills have their place in a machine shop, replaceable-insert spade drills offer specific advantages for various holemaking operations on machining centers and lathes.
Read MoreMicromachining Fundamentals
A number of elements must come together to establish an effective process for machining at a micro level. Here we consider four.
Read MoreData Matrix Codes Offer Cutting Tool Traceability
A company’s quest to discover errors in a manufacturing process has led to printing data matrix codes on its cutting tools that provide a wealth of information for both the user and this cutting tool manufacturer.
Read MoreProducing Micro Screws for the Watch Industry
Cutting tools play a key role in machining tiny screws on Swiss-type lathes for this Switzerland-based watch manufacturer.
Read MoreRead Next
5 Aspects of PMTS I Appreciate
The three-day edition of the 2025 Precision Machining Technology Show kicks off at the start of April. I’ll be there, and here are some reasons why.
Read MoreA Tooling Workshop Worth a Visit
Marubeni Citizen-Cincom’s tooling and accessory workshop offers a chance to learn more about ancillary devices that can boost machining efficiency and capability.
Read MoreDo You Have Single Points of Failure?
Plans need to be in place before a catastrophic event occurs.
Read More
















.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)








