Broaching On A Lathe
Producing a keyway, spline or similar longitudinal feature on a turned part usually necessitates an additional, time-consuming, secondary operation on a broaching or slotting machine. That means moving the part to and from a secondary operation, an extra setup, additional labor and hourly machine costs and all of the other headaches that go with secondary operations.
Producing a keyway, spline or similar longitudinal feature on a turned part usually necessitates an additional, time-consuming, secondary operation on a broaching or slotting machine. That means moving the part to and from a secondary operation, an extra setup, additional labor and hourly machine costs and all of the other headaches that go with secondary operations.
That is, assuming that you have the secondary machine. Grooves are made in so many different sizes and shapes that it is impractical for most shops to own their own machines and tooling. Many shops send out grooving work to firms that specialize in it, which increases the cost of the job accordingly.
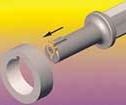
Now, however, you may be able to produce those grooves on a CNC lathe, in the same setup used to produce the other features of the part. Horn USA, Inc. (Franklin, Tennessee), a producer of grooving tools for milling and turning machines, has introduced a line of tools designed to permit keyways, grooves and similar features to be machined directly on a CNC lathe. The tool is mounted on the machine’s tool turret with the other turning and rotary tools. It is fed into the workpiece with a reciprocating motion and is continuously adjusted by the machine’s CNC in the X and Y axes as required to produce the necessary slot width and depth. Parts that require several grooves spaced at regular intervals on the circumference of a bore will require that the CNC lathe have a C axis to perform the required indexing of the part.
The insert-type broaching tools have a round shank with broad flat clamping surfaces that are 90 degrees apart to permit mounting the tool on any type of CNC lathe. Other shanks or system receivers, such as DI, Capto or HSK, are also available.
Because the process takes advantage of the movement capabilities of the CNC lathe, a modest amount of tooling can be used to produce a wide range of groove sizes. For example, the company’s S105 tool system can be used to produce slots up to 4 mm wide by 12 mm or 15 mm long, in some cases with unlimited depth. An S117 tool system is available for grooves greater than 4 mm wide. The standard reach length range on System S117 is 40 mm or 50 mm, depending on the holder type. Horn stocks standard inserts with a range of corner radii and tolerance classes for the broaching tools.
Although the broaching rates obtained with a CNC lathe are probably less than that of a dedicated broaching or slotting machine, being able to perform the operation in house and perform it in the same setup with the other turning and milling operations adds considerably to a shop’s flexibility. The producer recommends the broaching tools for one-of-a-kind jobs, prototype work and small batch production.
Oil-based coolants or emulsions are recommended for use with the broaching tools. In addition to flushing chips from the bore, the oil-based coolants have a lubricating effect that improves the groove’s surface properties and promotes longer tool life. Where the application permits, the broaching operation should be performed with the tool at the 12 o’clock position so that the chips produced during cutting do not negatively affect the broaching cycle.
A brochure is available from the company that describes the complete line of broaching tools for CNC lathes. Toolholder and insert dimensions along with tooling recommendations for various groove sizes are provided.
Related Content
Micromachining Fundamentals
A number of elements must come together to establish an effective process for machining at a micro level. Here we consider four.
Read MoreProducing Micro Screws for the Watch Industry
Cutting tools play a key role in machining tiny screws on Swiss-type lathes for this Switzerland-based watch manufacturer.
Read MoreNew Cutting Tool Technology Discovered at Paul Horn Open House
During a tour of the company’s campus in Tubingen, Germany, I and more than 3,000+ others were introduced to a number of new advances the company has made in cutting tool technology particularly as it relates to the medical industry.
Read MoreTool Path Improves Chip Management for Swiss-Type Lathes
This simple change to a Swiss-type turning machine’s tool path can dramatically improve its ability to manage chips.
Read MoreRead Next
5 Aspects of PMTS I Appreciate
The three-day edition of the 2025 Precision Machining Technology Show kicks off at the start of April. I’ll be there, and here are some reasons why.
Read MoreDo You Have Single Points of Failure?
Plans need to be in place before a catastrophic event occurs.
Read MoreEmerging Leaders Nominations Now Open
Here’s your chance to highlight a young person in your manufacturing business who is on the path to be a future leader moving your company forward.
Read More.png;maxWidth=970;quality=90)












.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)











