Automatically Optimize Your CNC Machining Feed Rates
New feed-rate-optimization technology can enable CAM programmers to reduce cycle times and increase tool life for milling and turning operations.

The Force module within Vericut can determine optimal feed rates throughout an NC program, speeding up where possible and slowing down when necessary to keep keeping cutting forces consistent. (Photo courtesy of CGTech.)
CAM programmers are constantly looking for ways to optimize tool paths and increase tool life. One school of thought for doing that is to maintain constant chip thickness throughout a cut, instead of a constant feed rate. That way, cutters engage with the same amount of material and encounter consistent cutting forces. “Force,” a new module within CGTech’s Vericut suite of toolpath simulation, verification and optimization software products, offers a way to automatically do that.
Pete Haas, Vericut product specialist, says Force achieves what feed rate calculators cannot and what manufacturers have been trying to implement for many years. That is, true constant-chip-thickness machining. “Instead of maintaining a constant feed rate throughout the cut in which chip thickness changes as the tool encounters varying amounts of material, Force speeds up or slows down to keep cutting forces steady,” he explains. “It’s very similar to how a machinist might dial the feed rate override up or down based on the sounds coming out of the machine, except that Force does it proactively and more effectively, rather than reacting to cutting noise levels.”
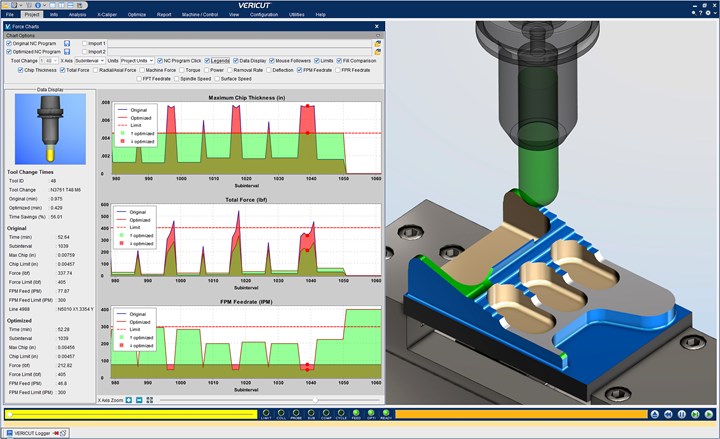
The module slows feed rates when cutting forces or spindle power demands are excessive, and breaks motions into smaller blocks as needed to both maximize chip thickness and keep it consistent throughout the cut. (Image courtesy of CG Tech.)
Force is a physics-based NC program optimization module that enables Vericut to analyze and optimize cutting conditions throughout NC program operations. For milling and turning alike, it automatically analyzes the tool path and compares the expected machining forces against a material-specific database. It then uses these values to determine optimal feed rates throughout the program, speeding up where possible and slowing down when necessary to keep keeping cutting forces consistent. It slows down when cutting forces or spindle power demands are excessive, and breaks motions into smaller blocks as needed to both maximize chip thickness and keep it consistent throughout the cut. All of this information is clearly visible to programmers, enabling them to see metal removal rates, tool deflection, power and torque levels, and more. Rather than overwriting the existing NC file, the module creates a separate .opti file. Force can then display the original file beside the .opti file for visual comparison.
It determines optimal feed rates throughout the program, speeding up where possible and slowing down when necessary to keep keeping cutting forces consistent.
John Giraldo, aerospace engineer with cutting tool manufacturer Sandvik Coromant, has used Vericut for a number of years to simulate NC tool paths to avoid machine crashes. Mr. Giraldo also works with many of the industry’s leading CAM systems, so he is quite familiar with modern programming technology. He is no stranger to toolpath optimization or customers coming to him with their problem jobs, difficult materials and challenging workpiece geometries.
During a recent test of the Force module, Mr. Giraldo says he was able to reduce a part program he had already optimized by an additional 40%. He also used Force to help a customer having a problem machining Haynes 282, a challenging nickel-based alloy.
The customer was using a trochoidal tool path (a method of milling that drives cutters in circular movements with lighter radial engagement at higher feed rates) to machine a deep pocket in a cylindrical casing. However, his customer was burning two end mills per pocket. By applying the Force module, one tool could complete five pockets and cycle time was reduced by 25%.
According to CGTech, Force has been developed over the last few years through actual on-machine testing, first with an advanced manufacturing research center, and then using its own dynamometer force measurement system. That testing continues today at Okuma America’s facility in Charlotte, North Carolina. “CGTech set up dyno equipment on some of our CNC lathes and machining centers, says Wade Anderson, Okuma product specialist sales manager. “We are taking cuts on different materials using a range of speeds and feeds, and measuring how much force is encountered for each cut. It’s a unique approach, and great to see because I know it’s going to help CGTech, cutting tool manufacturers such as Sandvik Coromant, and Okuma customers alike.”
Material Difference
The ability to create Force material files has recently become available via a software option called “Force Calibration.” Mr. Haas says this will not only enable users to fine-tune Force optimization based on their specific cutting tools and operating parameters but also addresses the needs of those in aerospace, medical, nuclear and other industries using proprietary materials in which details cannot be shared.

CGTech’s Pete Haas (right) and Okuma Principal Engineer Chris Davala have collaborated on Force optimization projects. The module can be used for both milling and turning operations. (Photo courtesy of CG Tech.)
He also says that the payback for Force can be fast, noting that many shops achieve a return on investment within 3 to 6 months, depending on part type and quantity. “But it’s not just about going faster or making more money,” he adds. “Force-optimized programs are safe because the software protects the NC program from machining excesses using programmer-defined limits on feed rate, cutting forces, power consumption and tool deflection. As a result, we have consistently seen significantly reduced cycle times, greatly improved tool life thanks to less heat and rubbing, and the cutting tool is now utilized to its full performance potential. Plus, as with Vericut itself, Force works with any machine tool and any NC program, whether it’s newly created or a legacy file from 10 years ago.”
Related Content
What Is Trochoidal Turning? How Might Shops Benefit From It?
While trochoidal milling might be a more well-known toolpath strategy, trochoidal turning can offer similar benefits such as high material removal rates especially for rough-turning operations.
Read MoreWho Are the DFM Consultants? You Are.
Modern shops are bolstering their engineering staff to better offer design for manufacturability advice to their customers. Here, one industry expert suggests ways to develop a common language between manufacturing and engineering.
Read MoreLone Shop Machinist Benefits From Five-Axis CAM Modules
This California shop owner applies five-axis strategies for more efficient milling of parts with challenging geometries, free-form surfaces and deep cavities.
Read MoreSoftware Controls Chip Breaking in Thread Turning Operations
This cutting tool manufacturer has developed a software module for chip control of thread turning operations in virtually any CNC lathe, even for older machines, using specific tooling and software.
Read MoreRead Next
Emerging Leaders Nominations Now Open
Here’s your chance to highlight a young person in your manufacturing business who is on the path to be a future leader moving your company forward.
Read More5 Aspects of PMTS I Appreciate
The three-day edition of the 2025 Precision Machining Technology Show kicks off at the start of April. I’ll be there, and here are some reasons why.
Read MoreA Tooling Workshop Worth a Visit
Marubeni Citizen-Cincom’s tooling and accessory workshop offers a chance to learn more about ancillary devices that can boost machining efficiency and capability.
Read More













.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)









