Investing in a Computerized Maintenance Management System
A computerized maintenance management system is a valuable tool to help automate preventive maintenance schedules on operational equipment.
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) is a valuable tool to help automate preventive maintenance (PM) schedules on operational equipment. Using a CMMS can improve the bottom line through increased labor efficiency, enhanced asset effectiveness, certification assistance with government agencies and certifying organizations (such as ISO, OSHA, JCAHO, FDA, and DOE), liability protection and more. A well conceived CMMS software package, written by software programmers who take the time to understand the needs of facilities, CNC machines and other equipment maintenance and operations professionals, can be a fundamental contributor to efficiency and best practices.
CMMS Functions
A CMMS monitors a variety of meter readings, including pressure, temperature, voltage, and hours run, and helps operators communicate when maintenance should be completed. Improved preventive maintenance planning can drastically improve the efficiency of any asset. Most leading CMMS software packages interface directly to CNC machines to collect data and generate PM schedules based on hourly run times instead of calendar periods, ensuring PM schedules are completed at optimal times. This results in a more efficient use of staff, reduced downtime and lower maintenance costs.
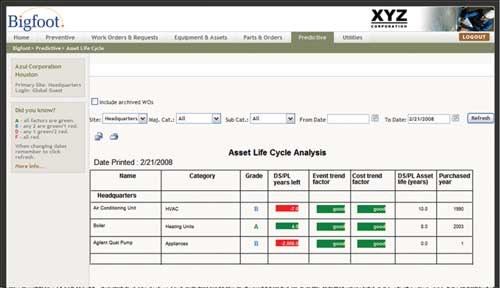
A CMMS can also track equipment history and grade performance over time. Instead of automatically projecting capital expenses to replace old equipment, CMMS software identifies which assets are poor performers by ranking every component. Surprisingly, a newer asset could be consuming more energy by failing frequently and costing more to repair over time. An asset would be retired or replaced based on several factors: frequency of failure, energy consumption, frequency of work orders, cost trends, and so on. Using CMMS software, a maintenance manager can be proactive about his maintenance plan and reduce capital expenditures.
The benefit of using the software is to reduce equipment downtime, minimize equipment and cost repairs, maximize equipment reliability and increase efficiency. Most users have used paper, Microsoft Excel or Outlook to keep track of when maintenance is required. But these methods have limitations. The implementation time for the CMMS Software can be completed in a few days, and the savings can be dramatic on the bottom line.
Overseeing Production
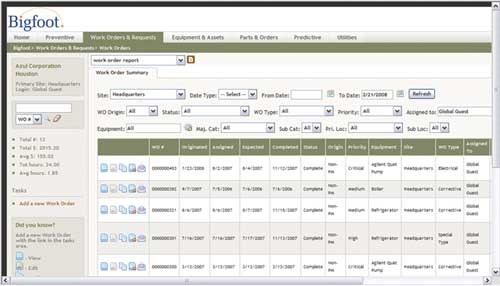
To fill this need for automating PM schedules, Shop Floor Automations offers Bigfoot, designed for maintenance operations seeking robust functionality and ease of use. Benefits of the software include scheduling, managing, analyzing and reporting on all aspects of maintenance, including preventive and predictive maintenance, work orders, maintenance requests, inventory and barcoding.
The software’s automatic PM reminders prevent PMs from falling through the cracks, and therefore, reduce equipment downtime. Even more time can be saved through the use of maintenance request forms, which shield maintenance department personnel from phone calls and e-mails about non-emergency maintenance requests.
Reporting and analysis tools allow the user to identify what work has been done on specific equipment over time and what work is still outstanding. The cost of equipment maintenance is tracked as well as statistics for machine downtime and reasons that it is not running.
Two versions of Bigfoot are available. The traditional, client-server edition is designed for single- or multi-user installations and provides a fast shop control with either an MS Access or MS SQL server backend database. The internet edition is completely Web-based and can be deployed anywhere. Users can manage any number of sites locally or around the world.
Related Content
High-Volume Machine Shop Automates Secondary Ops
An Ohio contract shop added a compact, self-loading CNC lathe to perform unattended secondary ops on a part for a key customer rather than running it on a manually loaded chucker.
Read MorePursuit of Parts Collector Spearheads New Enterprise
While searching for a small parts accumulator for Swiss-type lathes, this machine shop CEO not only found what he was looking for but also discovered how to become a distributor for the unique product.
Read MoreZoller Event Shines Lights on Shopfloor Connectivity
The company’s open house event highlighted smart manufacturing solutions from CAM to part.
Read MoreInside the Premium Machine Shop Making Fasteners
AMPG can’t help but take risks — its management doesn’t know how to run machines. But these risks have enabled it to become a runaway success in its market.
Read MoreRead Next
The Case For Integrated Control Of Machining Operations
An integrated software system automates a decision-making process that helps a machinist inspect parts on a timely basis, offset or change tools and appeal to engineers for improvement of process design.
Read MoreA Tooling Workshop Worth a Visit
Marubeni Citizen-Cincom’s tooling and accessory workshop offers a chance to learn more about ancillary devices that can boost machining efficiency and capability.
Read MoreEmerging Leaders Nominations Now Open
Here’s your chance to highlight a young person in your manufacturing business who is on the path to be a future leader moving your company forward.
Read More













.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)









